What is Astigmatism in Lasers?
Astigmatism in laser beams is an optical aberration where the beam does not focus to a single point due to differences in the curvature of the optical elements in the horizontal and vertical planes. This results in the beam having different focal points for the horizontal and vertical components, leading to an elliptical or distorted beam shape
Astigmatism can be quantified using the difference in the Rayleigh ranges for the horizontal and vertical components. The Rayleigh range (zR) is the distance over which the beam radius increases by a factor of √2. The Rayleigh range is defined as:
zR=πW02/λ
where:
- W0 is the beam waist (where the beam diameter is at its minimum).
- λ is the wavelength of the laser.
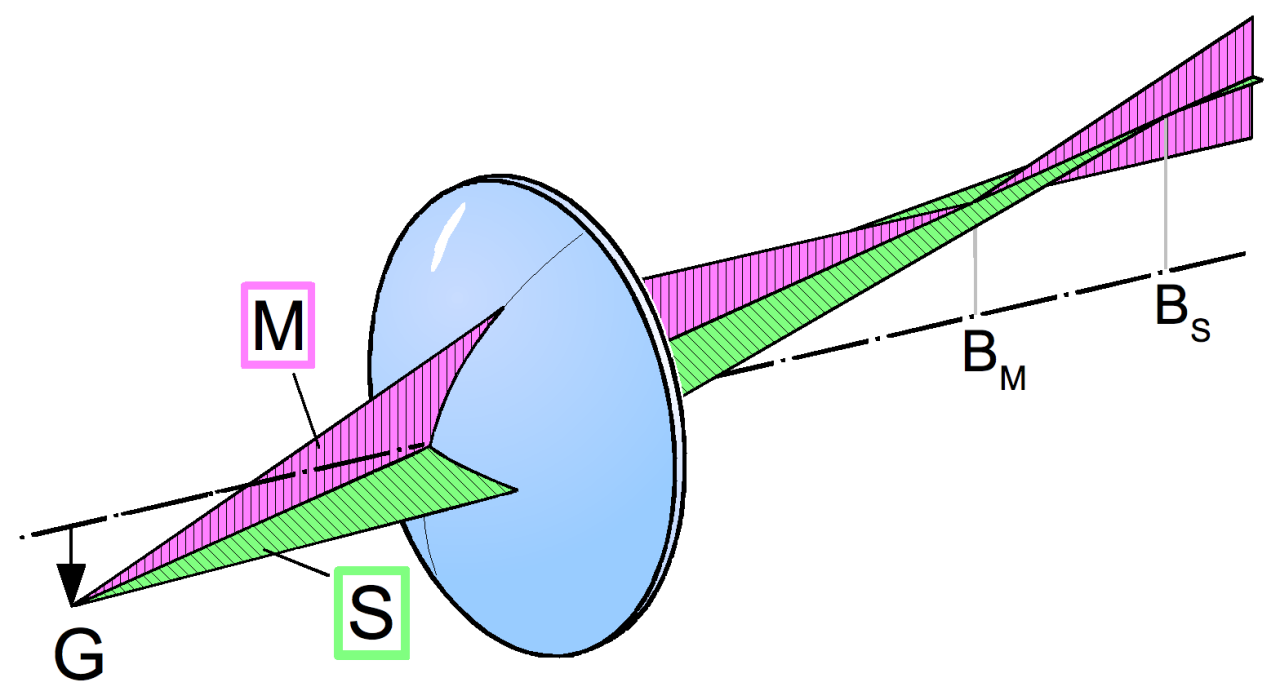
For an astigmatic beam, the Rayleigh ranges in the horizontal (zRx )and vertical (zRy) directions are different, leading to:
A= (( zRx – zRy)/( zRx + zRy))
where:
- zRx is the Rayleigh range in the horizontal direction.
- zRy is the Rayleigh range in the vertical direction.
Why is it Important to Measure Astigmatism Accurately?
Accurate measurement of astigmatism in laser beams is crucial for several reasons:
- For applications requiring high precision, such as medical procedures and semiconductor manufacturing, even minor astigmatism can lead to significant errors. Accurate measurement makes sure that the laser beam maintains its intended shape and focus.
- Astigmatism causes inconsistent energy distribution across the laser beam, leading to uneven results. Accurate measurement and correction ensure consistent performance, reducing defects and improving reliability.
- Astigmatic beams require continuous re-alignment, leading to higher operational costs.
- In medical applications, the safety and reliability of laser systems are paramount. Accurate measurement of astigmatism ensures that the laser beam is safe and effective for procedures.
Industry Processes Requiring Stigmatic Beams
Several industry processes rely on stigmatic (non-astigmatic) beams for optimal performance:
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Many processes in semiconductor manufacturing require highly precise and focused beams to create intricate patterns on wafers.
Medical Procedures: Precision is critical in medical applications such as LASIK eye surgery, where astigmatism can lead to issues.
Industrial Cutting and Welding: Stigmatic beams ensure precise energy delivery in cutting and welding applications, leads to stronger welds and precise cuts.
Laser Trends: Large Diameter Beams, UV Beams, and Extended Rayleigh Range
Large Diameter Beams: The trend towards using larger laser beams is driven by the need for higher power and efficiency. Larger beams can deliver more energy over a broader area, making them suitable for tasks such as cutting thick materials and performing high-precision surgeries.
UV Beams: Ultraviolet (UV) lasers, with their shorter wavelengths, are increasingly used in applications requiring high precision, such as semiconductor manufacturing and medical imaging. However, UV beams are more sensitive to imperfections in optical components, leading to astigmatism. The shorter wavelength also requires higher precision in manufacturing and alignment, making accurate measurement and correction essential.
Extended Rayleigh Range: The Rayleigh range (zR) increases with larger beam waists (W0), allowing the beam to stay focused over greater distances. This extended range is crucial for maintaining beam quality and precision in applications such as LiDAR systems, large-scale manufacturing, and optical communications.
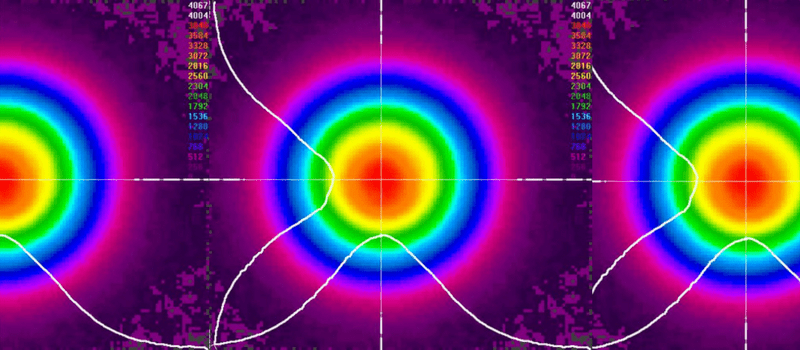
Systematic Errors in Measurement Devices and Their Impact
Systematic errors arise from calibration offsets, optical misalignments and defects in optical components. These errors can significantly affect the accuracy of astigmatism measurements. BeamSquared SP204S-PRO specifically corrects these errors and provides industry leading 3% accuracy in astigmatism measurement.
Here is how we achieve it:
- Optics Improvement:
BeamSquared SP204S-PRO uses high-quality, defect free optical components designed to minimize distortions. The optical alignment of components is improved to minimize errors.
- State-of-the-Art Astigmatism Correction Algorithm
The remanent astigmatism of the device is corrected using a specialized algorithm developed during the production process. This algorithm characterizes the device and applies corrections across the entire spectrum in which the device operates.
- Special Lens Calibrations
BeamSquared SP204S-PRO features specially calibrated long focal length lenses. These lenses are calibrated to achieve much higher accuracies, significantly reducing errors associated with focal length discrepancies. The combination of longer focal length lenses and precise calibration ensures minimal contribution to measurement errors.
With all these improvements, Beamsquared Pro can achieve 3% error in astigmatism measurement.

How this accuracy improves customer outcome:
Enhanced Device-to-Device Consistency
BeamSquared Pro offers exceptional device-to-device consistency with laser astigmatism measurement, which is critical for maintaining uniformity across different production batches of lasers.
Lower Operational Costs: By ensuring accurate measurements and reducing the need for frequent recalibrations and adjustments, BeamSquared SP204S-PRO helps lower operational costs.
Innovation and Development: With its high measurement confidence, BeamSquared Pro enables manufacturers to innovate and develop new laser technologies and applications.
BeamSquared SP204S-PRO addresses laser astigmatism with high accuracy through advanced optics, specialized calibration, and state-of-the-art correction algorithms. This leads to precise, consistent laser astigmatism measurements throughout, reducing operational costs and enabling innovation. Accurate astigmatism measurement is crucial for high-precision tasks in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, medical procedures, and materials processing.







Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *